Operation Support Systems (OSS) originally emerged in the telecommunications industry as a tool for remote management and ensuring uninterrupted operation of mobile communication. The main goal of implementing such systems is to reduce the operational costs of the provider and optimize the cellular network, enhancing its efficiency, performance, and availability.
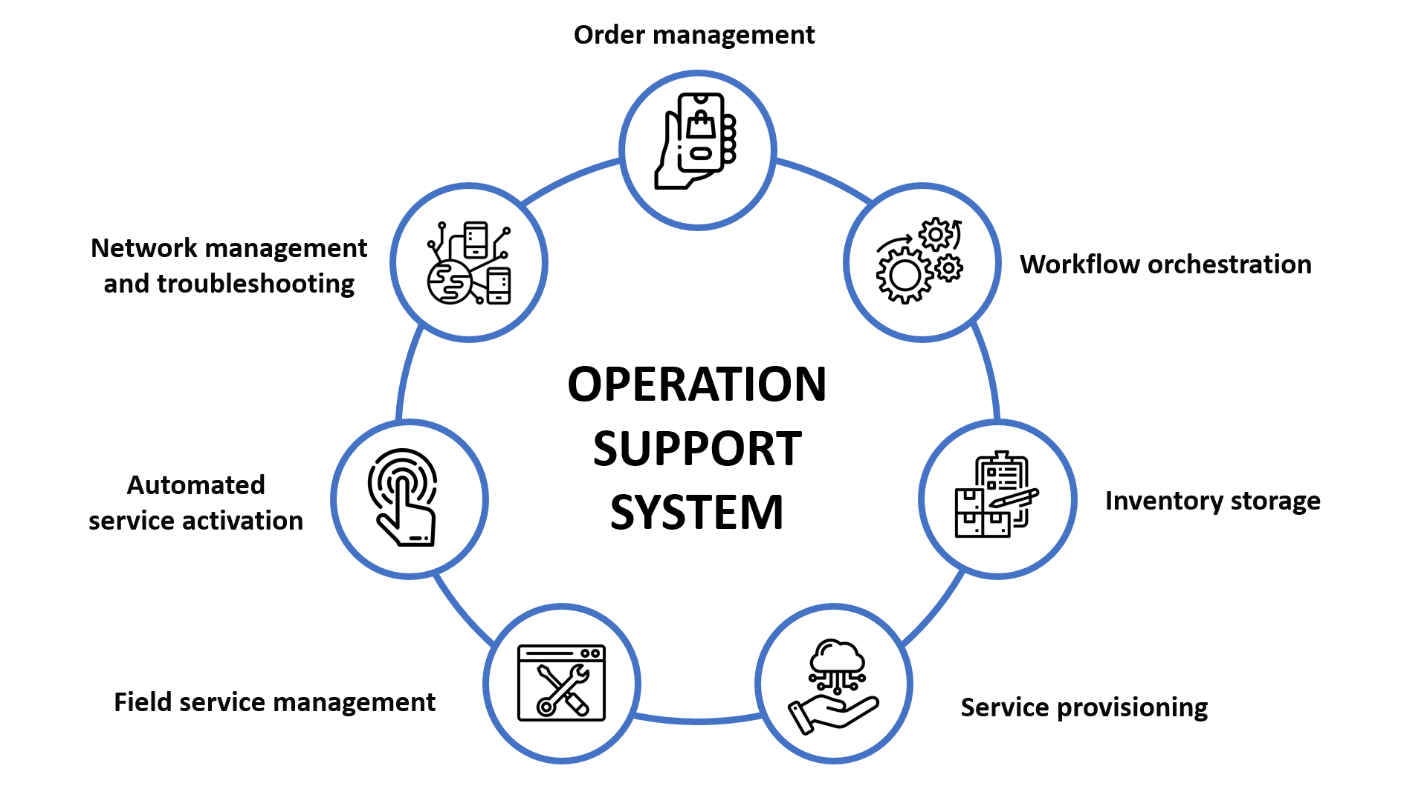
The functions of Operation Support Systems include:
Order Management:
OSS systems help process orders and monitor the accuracy of information transmission, ensuring process integrity and preventing the transmission of incorrect or incomplete orders.
Work Process Orchestration:
Operation support systems include a work process mechanism that regulates data transmission between the components of a cellular network and generates commands for each subsystem to perform its function in the correct order and at the specified time.
Network Inventory:
During order processing, the system monitors the availability, performance, and readiness of equipment to deliver cellular services.
Service Provisioning:
OSS systems control physical equipment and define service provisioning schemes that need to be allocated for future activation.
Service Assurance:
Operation Support Systems store information about the locations of network components and devices, equipment maintenance.
Automated Service Activation:
When a service needs to be provided, OSS automatically initiates connections with relevant network elements such as switches, multiplexers, and cross-connects.
Network Management and Fault Remediation:
OSS is responsible for comprehensive network supervision, including traffic and performance monitoring, network self-diagnostics and notifications, creation of tasks for technical staff to resolve faults.
Operation Support System Architecture
Major telecommunications equipment manufacturers typically provide OSS systems tailored to their own equipment. Among the top solutions identified by research company Gartner are several well-known manufacturers such as Nokia, Huawei, and Ericsson.
However, there are cases where customized solutions are required, such as:
Unique Business Processes:
If a company has specific or unique business processes that cannot be supported by ready-made OSS solutions, it is recommended to use custom development that caters to the company’s needs. This allows for the implementation of an operation support system that does not require compromises and fully aligns with the business requirements. One example could be a network of IoT devices.
Integration with Other Systems:
If a company already uses other systems, such as Customer Relationship Management (CRM) or Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) systems, it might be necessary to integrate the OSS system with them. In such cases, the integration may require custom development to ensure the interoperability of different systems and data exchange between them. For example, an operation support system that supports the devices of multiple mobile operators’ networks.
Extension of Functionality:
Off-the-shelf OSS solutions may not possess all the necessary functions for a specific company. In such cases, custom development allows for adding the required features and configuring the system to meet specific requirements.
When a company decides to implement an OSS system, it is important to conduct requirements analysis, assess available solutions, and determine if they sufficiently meet the company’s needs. If custom development is necessary, it is advisable to consult specialists or developers capable of creating and configuring an operation support system that effectively supports the company’s business processes.
Epol Soft develops, enhances, and supports Operation Support Systems for telecommunications companies. For detailed information, please visit the link.

